Understanding the difference between an MRI and a CT scan is essential when you are trying to make informed decisions about your health. Both imaging tests play an important role in diagnosing medical conditions but they work in very different ways. If you have ever wondered which scan is better, what each scan shows or why a doctor would recommend one over the other, this guide explains everything clearly.
MRI Scan
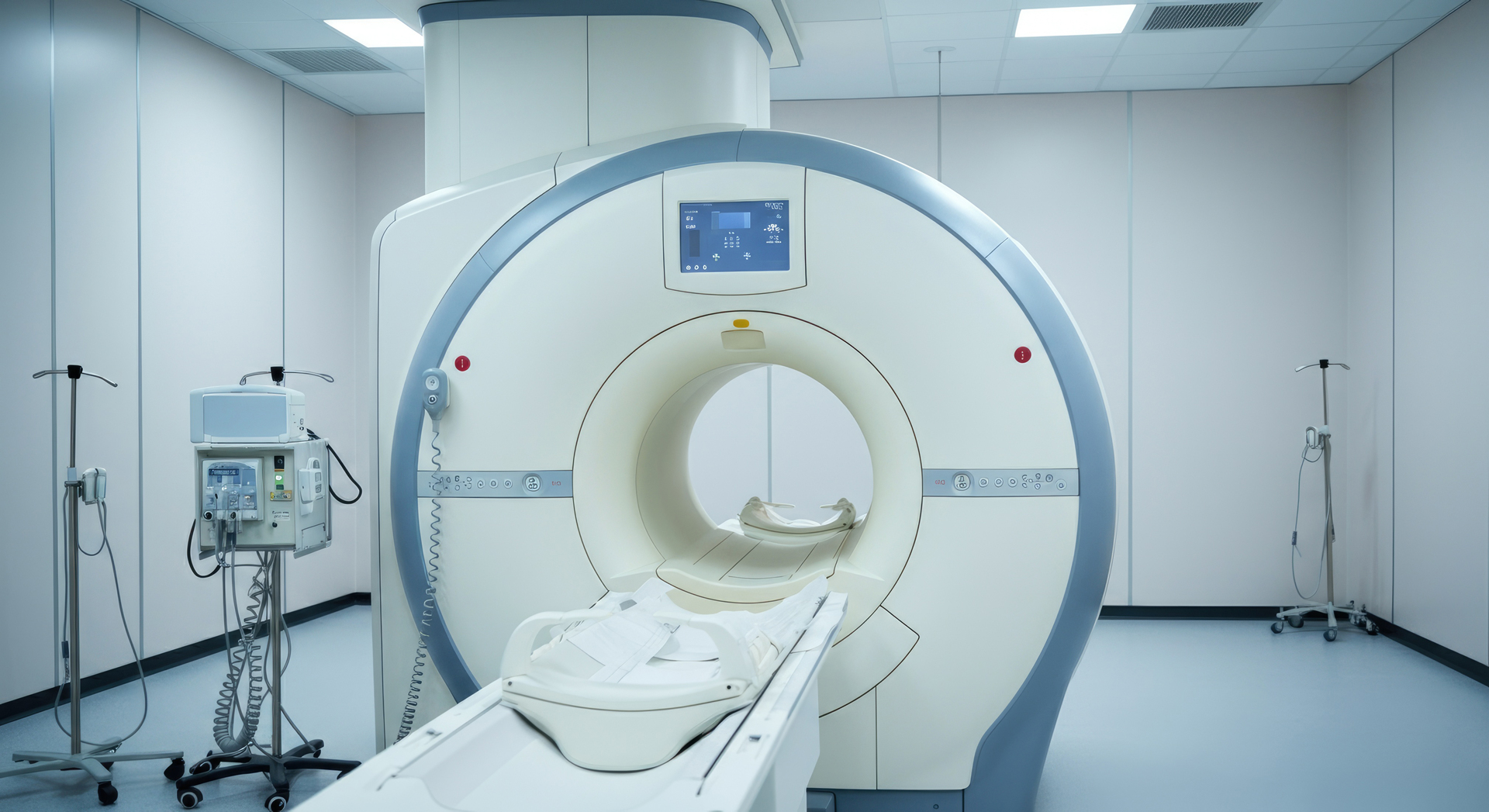
An MRI scan, also known as Magnetic Resonance Imaging, uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and soft tissues. MRI is especially effective for examining the brain, spinal cord, nerves, ligaments, cartilage, and internal organs. It produces very clear images without using radiation, making it ideal for patients who need repeated imaging or more detailed soft-tissue assessment.
MRI scans are also commonly used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including joint, muscle, and ligament injuries (such as those assessed with a Knee MRI or Shoulder MRI), heart and blood vessel conditions (Cardiac MRI), tumours or abnormal growths, and organ-related issues involving the liver, kidneys, or abdomen (Abdominal MRI).
CT Scan Explained
A CT scan also called Computed Tomography uses X ray technology to produce fast cross sectional images of the body. It is very effective at detecting bone fractures, internal bleeding, lung problems and cancers. CT scans are quick, widely available and excellent for emergencies or situations where every second counts.
Key Differences Between an MRI and a CT Scan
Technology:
MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate images, whereas CT uses X-rays to create cross-sectional pictures. This means MRI involves no radiation, while CT scans do expose patients to a small amount of ionising radiation.
Best For:
MRI scans excel at imaging soft tissues: organs, muscles, nerves, brain, spinal cord, ligaments and tendons. CT scans are typically better for bone, detecting fractures, and scanning the chest, abdomen, or in emergency situations (like spotting internal bleeding or stroke).
Image Detail:
An MRI generally provides higher contrast and detail for soft tissue structures and can show subtle differences in tissues that a CT might miss. CT images are very detailed for bone structures and can still show organs and tissues, but not with the same soft tissue contrast as MRI.
Scan Time:
A CT scan is much faster, usually just a few minutes for the scan itself. An MRI scan takes longer, often 15 – 45 minutes or more depending on the area being scanned, because it composes many detailed images.
Patient Experience:
MRI machines are a tunnel like tube and can be loud during operation (you’ll wear ear protection). CT scanners are doughnut shaped rings and the procedure is quiet.
Cost and Availability:
MRI scans tend to cost more than CT scans because of the expensive equipment and longer scan times. CT scanners are common in most hospitals for quick diagnostics, whereas MRI machines are also widely available but may have longer waiting lists due to demand.
What Do MRI and CT Scans Show
Both MRI and CT scans can be used to identify a wide range of conditions but each excels in different areas. Choosing the right scan depends on the part of the body being examined and what your doctor is looking for.
What Can a CT Scan Show That an MRI Cannot
A CT scan can identify certain conditions faster than an MRI. These include complex bone fractures, lung diseases, kidney stones, chest trauma and internal bleeding. CT scans are also more reliable for imaging patients who cannot remain still for long periods such as those in emergency care.
What Can an MRI Show That a CT Scan Cannot
An MRI offers superior detail of soft tissue. It can detect very small tears in ligaments and tendons, subtle brain abnormalities, nerve damage and early stage tumours in organs like the liver and pancreas. MRI is also the best choice for assessing spinal discs, joint cartilage and detailed brain mapping.
CT Scan vs MRI The Procedure
What to Expect During a CT Scan
A CT scan is very quick. You lie on a table that moves through a circular scanner while a series of X rays capture multiple images. Most scans take less than ten minutes and you can usually go straight home afterwards.
What to Expect During an MRI Scan
An MRI scan takes longer usually between twenty and sixty minutes depending on the area being scanned. You lie inside a large tube like machine while magnetic waves create the images. The scan is painless but can be noisy so ear protection is normally provided.
Pros and Cons of CT Scans vs MRI Scans
MRI Advantages
MRI Disadvantages
CT Scan Advantages
CT Scan Disadvantages
Choose the Right Scan for You
Choosing between an MRI and CT scan does not need to be confusing. At Vital Scan Health you can receive expert guidance to help you understand which scan is most suitable for your symptoms. Whether you want fast results or the highest level of image detail, you can choose a scan that supports your health and wellbeing.
MRI vs CT Scan Frequently Asked Questions
Book Your MRI Scan in Milton Keynes
Choosing between an MRI and CT scan does not need to be confusing. At Vital Scan Health you can receive expert guidance to help you understand which scan is most suitable for your symptoms.
Whether you want fast results or the highest level of image detail, you can choose a scan that supports your health and wellbeing.
Book MRI Scan or call 01908 755556 if you’d prefer to speak to someone directly.
